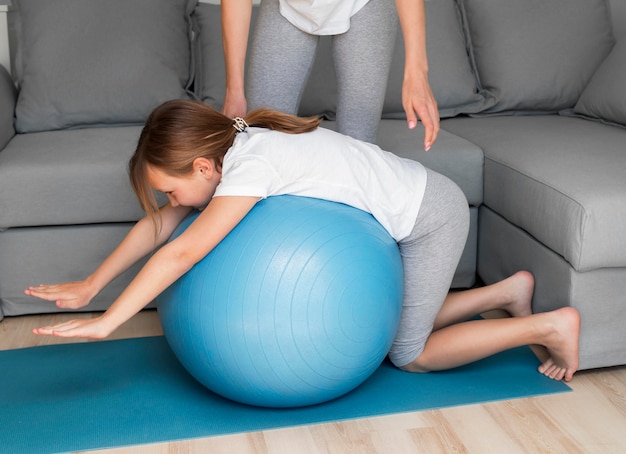
The Swiss ball, also known as a fitball or gym ball, is a versatile tool used in workouts for various purposes. It can help with muscle exercises like abdominal crunches, flexibility exercises, joint mobility, proprioception, and balance. This article explains why the Swiss ball is effective and how it aids in fitness training.
The Evolution and Application of the Swiss Ball
Initially created as a children’s toy in the early 1960s, the Swiss ball was soon recognized for its therapeutic benefits. It is particularly effective for enhancing sensitivity to muscle and nerve stimuli and improving joint stability.
Nowadays, the Swiss ball is widely used in athletic training and personal workouts. It’s incorporated into routines for muscle strengthening and coordination because it significantly impacts certain physiological mechanisms through the stresses it creates.
Understanding Proprioception
Proprioception is crucial to understanding the benefits of the Swiss ball. Often called the “sixth sense,” proprioception helps us sense and control our movements and body positions. Unlike the traditional senses that connect us to the outer world, proprioception gives internal feedback about where our limbs and body are in space. This system is vital for everyday activities, from walking to complex sports moves.
Proprioception depends on proprioceptors in our muscles, tendons, and joints. These include neuromuscular spindles, golgi tendon organs, and joint receptors. Along with skin receptors, they provide a full picture of our body鈥檚 position and movements, ensuring coordinated physical responses.
Neuromuscular Spindles
Located in the muscles, these receptors are sensitive to the length and intensity of muscle stretch. When activated, they trigger muscle contraction, a reflex known as the myotatic reflex.
Golgi Tendon Organs
Found at the muscle-tendon junction, these receptors respond to tendon stretch caused by muscle contraction. When activated, they send signals to inhibit muscle contraction. This reverse myotatic reflex protects the body from excessive tendon tension.
Joint Receptors
These receptors provide information about joint angle, movement speed, and joint compression. They collect extensive data about body position and movement, aiding in movement control.
The Swiss Ball and Proprioception
The Swiss ball stimulates these reflexes and receptors through its instability, which demands constant adjustment. The difficulty can be tweaked by changing the ball’s firmness or size. Softening or enlarging the ball makes exercises easier, while hardening or reducing its size increases the challenge.
To get the most out of Swiss ball training, exercises should be tailored to an individual鈥檚 needs, considering factors like duration, difficulty, and overall training load.
Benefits of the Swiss Ball
Adding a Swiss ball to your workouts can boost your fitness routine with several advantages:
1. Enhanced Proprioception: It helps improve your body’s ability to sense and manage its position in space, important for both everyday activities and sports.
2. Engagement of Core and Stabilizing Muscles: The ball effectively activates core and stabilizing muscles often missed in regular workouts, helping with posture and injury prevention.
3. Increased Strength and Improved Joint Health: Regular exercises with the ball boost overall strength and joint health due to the dynamic and varied movements it encourages.
4. Improved Balance and Coordination: Exercising on the unstable surface of the ball enhances balance and coordination, which benefits daily activities and sports performance.
In summary, the Swiss ball is a powerful fitness tool that improves proprioception, muscle strength, joint health, and overall physical performance. Whether you’re an athlete or just looking to stay active, incorporating the Swiss ball into your fitness routine can offer significant benefits.